
Applications for the LAMP Fellowship 2025-26 will open on December 1, 2024. Sign up here to be notified when applications open.
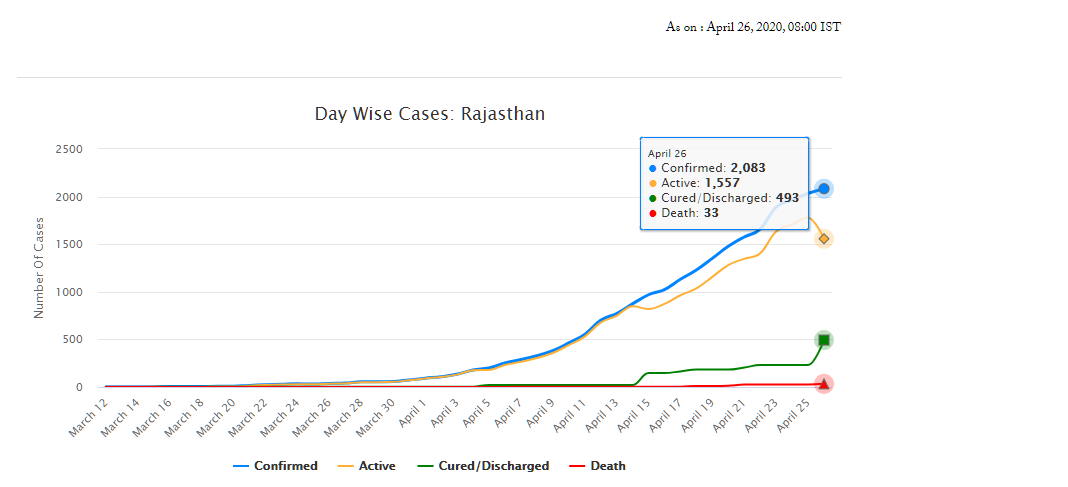
As of April 26, Rajasthan has 2,083 confirmed cases of COVID-19 (fifth highest in the country), of which 493 have recovered and 33 have died. On March 18, the Rajasthan government had declared a state-wide curfew till March 31, to check the spread of the disease. A nation-wide lockdown has also been in place since March 25 and is currently, extended up to May 3. The state has announced several policy decisions to prevent the spread of the virus and provide relief for those affected by it. This blog summarises the key policy measures taken by the Government of Rajasthan in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Early measures for containment
Between late January and early February, Rajasthan Government’s measures were aimed towards identification, screening and testing, and constant monitoring of passenger arrivals from China. Instructions were also issued to district health officials for various prevention, treatment, & control related activities, such as (i) mandatory 28-day home isolation for all travellers from China, (ii) running awareness campaigns, and (iii) ensuring adequate supplies of Personal Protection Equipments (PPEs). Some of the other measures, taken prior to the state-wide lockdown, are summarised below:
Administrative measures
The government announced the formation of Rapid Response Teams (RRTs), at the medical college-level and at district-level on March 3 and 5, respectively.
The District Collector was appointed as the Nodal Officer for all COVID-19 containment activities. Control Rooms were to be opened at all Sub-divisional offices. The concerned officers were also directed to strengthen information dissemination mechanisms and tackle the menace of fake news.
Directives were issued on March 11 to rural health workers/officials to report for duty on Gazetted holidays. Further, government departments were shut down between March 22 and March 31. Only essential departments such as Health Services were allowed to function on a rotation basis at 50% capacity and special / emergency leaves were permitted.
Travel and Movement
Air travellers were to undergo 14-day home isolation and were also required to provide an undertaking for the same. Besides, those violating the mandated isolation/quarantine were liable to be punished under Section. 188 of the Indian Penal Code. Penalties are imposed under this section on persons for the willful violation of orders that have been duly passed by a public servant.
All institutions and establishments, such as (i) educational institutions, theatres, and gyms, (ii) anganwadis, (iii) bars, discos, libraries, restaurants etc, (iv) museums and tourist places, were directed to be shut down till March 31.
The daily Jan Sunwai at the Chief Minister’s residence was cancelled until further notice. Various government offices were directed to shut down and exams of schools and colleges were postponed.
On March 24, the government issued a state-wide ban on the movement of private vehicles till March 31.
Health Measures
Advisories regarding prevention and control measures were issued to: (i) District Collectors, regarding sample collection and transportation, hotels, and preparedness of hospitals, (ii) Police department, to stop using breath analysers, (iii) Private hospitals, regarding preparedness and monitoring activities, and (iv) Temple trusts, to disinfect their premises with chemicals.
The government issued Standard Operating Procedures for conducting mock drills in emergency response handling of COVID-19 cases. Training and capacity building measures were also initiated for (i) Railways, Army personnel etc and (ii) ASHA workers, through video conferencing.
A model micro-plan for containing local transmission of COVID was released. Key features of the plan include: (i) identification and mapping of affected areas, (ii) activities for prevention control, surveillance, and contact tracing, (iii) human resource management, including roles and responsibilities, (iv) various infrastructural and logistical support, such as hospitals, labs etc, and (v) communication and data management.
Resource Management: Private hospitals and medical colleges were instructed to reserve 25 % of beds for COVID-19 patients. They were also instructed to utilise faculty from the departments of Preventive and Social Medicine to conduct health education and awareness activities.
Over 6000 Students of nursing schools were employed in assisting the health department to conduct screening activities being conducted at public places, railways stations, bus stands etc.
Further, the government issued guidelines to ensure the rational use of PPEs.
Welfare Measures
The government announced financial assistance, in the form of encouragement grants, to health professionals engaged in treating COVID-19 patients.
Steps were also taken by the government to ensure speedy disbursal of pensions for February and March.
The government also initiated the replacement of the biometric authentication with an OTP process for distribution of ration via the Public Distribution System (PDS).
During the lockdown
State-wide curfew announced on March 18 has been followed by a nation-wide lockdown between March 25 and May 3. However, certain relaxations have been recommended by the state government from April 21 onwards. Some of the key measures undertaken during the lockdown period are:
Administrative Measures
Advisory groups and task forces were set up on – (i) COVID-19 prevention, (ii) Health and Economy, and (iii) Higher education. These groups will provide advice on the way forward for (i) prevention and containment activities, (ii) post-lockdown strategies and strategies to revive the economy, and (iii) to address the challenges facing the higher education sector respectively.
Services of retiring medical and paramedical professionals retiring between March and August have been extended till September 2020.
Essential Goods and Services
A Drug Supply Control Room was set up at the Rajasthan Pharmacy Council. This is to ensure uninterrupted supply of medicines during the lockdown and will also assist in facilitating home delivery of medicines.
The government permitted Fair Price Shops to sell products such as masalas, sanitisers, and hygiene products, in addition to food grains.
Village service cooperatives were declared as secondary markets to facilitate farmers to sell their produce near their own fields/villages during the lockdown.
A Whatsapp helpline was also set up for complaints regarding hoarding, black marketing, and overpricing.
Travel and Movement
Once lockdown was in place, the government issued instructions to identify, screen, and categorise people from other states who have travelled to Rajasthan. They were to be categorised into: (i) people displaying symptoms to be put in isolation wards, (ii) people over 60 years of age with symptoms and co-morbidities to be put in quarantine centres, and (iii) asymptomatic people to be home quarantined.
On March 28, the government announced the availability of buses to transport people during the lockdown. Further, stranded students in Kota were allowed to return to their respective states.
On April 2, a portal and a helpline were launched to help stranded foreign tourists and NRIs.
On April 11, an e-pass facility was launched for movement of people and vehicles.
Health Measures
To identify COVID-19 patients, district officials were instructed to monitor people with ARI/URI/Pneumonia or other breathing difficulties coming into hospital OPDs. Pharmacists were also instructed to not issue medicines for cold/cough without prescriptions.
A mobile app – Raj COVID Info – was developed by the government for tracking of quarantined people. Quarantined persons are required to send their selfie clicks at regular intervals, failing which a notification would be sent by the app. The app also provides a lot of information on COVID-19, such as the number of cases, and press releases by the government.
Due to the lockdown, people had restricted access to hospitals and treatment. Thus, instructions were issued to utilise Mobile Medical Vans for treatment/screening and also as mobile OPDs.
On April 20, a detailed action plan for prevention and control of COVID-19 was released. The report recommended: (i) preparation of a containment plan, (ii) formation of RRTs, (iii) testing protocols, (iv) setting up of control room and helpline, (v) designated quarantine centres and COVID-19 hospitals, (vi) roles and responsibilities, and (vii) other logistics.
Welfare Measures
The government issued instructions to make medicines available free of cost to senior citizens and other patients with chronic illnesses through the Chief Minister’s Free Medicine Scheme.
Rs 60 crore was allotted to Panchayati Raj Institutions to purchase PPEs and for other prevention activities.
A one-time cash transfer of Rs 1000 to over 15 lakh construction workers was announced. Similar cash transfer of Rs 1000 was announced for poor people who were deprived of livelihood during the lockdown, particularly those people with no social security benefits. Eligible families would be selected through the Aadhaar database. Further, an additional cash transfer of Rs 1500 to needy eligible families from different categories was announced.
The state also announced an aid of Rs 50 lakh to the families of frontline workers who lose their lives due to COVID-19.
To maintain social distancing, the government will conduct a door-to-door distribution of ration to select beneficiaries in rural areas of the state. The government also announced the distribution of free wheat for April, May, and June, under the National Food Security Act, 2013. Ration will also be distributed to stranded migrant families from Pakistan, living in the state.
The government announced free tractor & farming equipment on rent in tie-up with farming equipment manufacturers to assist economically weak small & marginal farmers.
Other Measures
Education: Project SMILE was launched to connect students and teachers online during the lockdown. Study material would be sent through specially formed Whatsapp groups. For each subject, 30-40 minute content videos have been prepared by the Education Department.
Industry: On April 18, new guidelines were issued for industries and enterprises to resume operations from April 20 onwards. Industries located in rural areas or export units / SEZs in municipal areas where accommodation facilities for workers are present, are allowed to function. Factories have been permitted to increase the working hours from 8 hours to 12 hours per day, to reduce the requirement of workers in factories. This exemption has been allowed for the next three months for factories operating at 60% to 65% of manpower capacity.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.
Several Rajya Sabha seats go to elections this year. The President and the Vice-President are also due to be elected by August. We analyse the impact of the recent State Assembly elections on the composition of the Rajya Sabha and the outcome of the Presidential polls. Rajya Sabha - How will its composition change? Since Rajya Sabha members are elected by the elected members of State Legislative Assemblies, a change in the composition of State Assemblies can affect the composition of Rajya Sabha. A total of 61 Rajya Sabha seats are up for election in April and July. This includes 10 seats from Uttar Pradesh and 1 seat from Uttarakhand. In light of the recent Assembly elections, we work out two scenarios to estimate the composition of Rajya Sabha in 2012. Members of Rajya Sabha are elected through the system of proportional representation by means of the Single Transferable Vote (STV). In an STV election, a candidate is required to achieve a certain minimum number of votes (called the 'quota') to be elected. (For more details on the STV system, click here) For instance, in the case of Uttar Pradesh (UP) 10 Rajya Sabha seats go to election this year. Candidates will be elected to these 10 seats by the 403 elected MLAs of the Uttar Pradesh State Assembly. Each MLA will rank the candidates based on his/ her preference. After successive rounds of elimination, candidates who are able to secure at least 37 {or 403/(10+1) } votes will be declared elected. In the new UP Assembly, Samajwadi Party (SP) has a total strength of 224 members. As a result, SP can elect at least 6 (or 224/37) Rajya Sabha MPs of its choice. BSP's strength of 80 will allow it to elect 2 (or 80/37) MPs to Rajya Sabha. Similarily, the BJP with a strength of 47 MLAs can have one candidate of its choice elected to the Rajya Sabha. This leaves 1 seat. The fate of this seat depends on the alliances that may be formed since no other party in UP has 37 or more seats in the Assembly. If the Congress (28 seats) and RLD (9 seats) join hands, they may be able to elect a candidate of their choice. We build two scenarios which give the likely range of seats for the major coalitions and parties. The actual result will likely fall between these scenarios, depending on alliances for each election. Of the two scenarios, Scenario II is better for the UPA. It is based on the assumption that the UPA is able to put together the necessary support/ alliances to get its candidates elected to seats with indeterminate status. Scenario I is based on the assumption that the UPA is not able to put together the required support. As a result, the seats in question get allocated to candidates from other parties/ coalitions. (See Notes for the composition of the coalitions) Composition of Rajya Sabha
| Party/ Coalition | Current composition | Scenario I | Scenario II |
| Total seats |
245 |
245 |
245 |
| UPA |
93 |
95 |
98 |
| NDA |
66 |
67 |
65 |
| Left |
19 |
14 |
14 |
| BSP |
18 |
15 |
15 |
| SP |
5 |
9 |
9 |
| BJD |
6 |
8 |
7 |
| AIADMK |
5 |
5 |
5 |
| Nominated |
7 |
12 |
12 |
| Others |
21 |
20 |
20 |
| Vacant |
5 |
0 |
0 |
It appears that there would not be a major change in the composition of the Rajya Sabha. Which party's candidate is likely to become the next President? The next Presidential election will be held in June or July. The electoral college for the Presidential election consists of the elected members of Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha and all Legislative Assemblies. Each MP/ MLA’s vote has a pre-determined value based on the population they represent. For instance, an MP's vote has a value of 708, an MLA from UP has a vote value of 208 and an MLA from Sikkim has a vote value of 7. (Note that all MPs, irrespective of the constituency or State they represent, have equal vote value) As is evident, changes in the composition of Assemblies in larger States such as UP can have a major impact on the outcome of the Presidential election. The elections to the office of the President are held through the system of proportional representation by means of STV (same as in the case of Rajya Sabha). The winning candidate must secure at least 50% of the total value of votes polled. (For details, refer to this Election Commission document). By this calculation, a candidate will need at least 5,48,507 votes to be elected as the President. If the UPA were to vote as a consolidated block, its vote tally would reach 4,50,555 votes under Scenario II (the one that is favourable for the UPA). Therefore, the UPA will have to seek alliances if it wants a candidate of its choice to be elected to the office of the President. Scenarios for Presidential elections (figures represent the value of votes available with each party/ coalition)
| Party/ Coalition | Scenario I | Scenario II |
| UPA |
4,48,431 |
4,50,555 |
| NDA |
3,05,328 |
3,03,912 |
| Left |
51,574 |
51,574 |
| BSP |
43,723 |
43,723 |
| SP |
69,651 |
69,651 |
| BJD |
30,923 |
30,215 |
| AIADMK |
36,216 |
36,216 |
| Others |
1,11,166 |
1,11,166 |
| Total |
10,97,012 |
10,97,012 |
| Minimum required to be elected |
5,48,507 |
5,48,507 |
What about the Vice-President? Elections to the office of the Vice-President (VP) will be held in July or August. The electoral college will consist of all members of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha (i.e. both elected and nominated). Unlike the Presidential elections, all votes will have an equal value of one. Like the President, the VP is also elected through the system of proportional representation by means of STV. The winning candidate must secure at least 50% of the total value of votes polled. Presently, two seats are vacant in the Lok Sabha. If we exclude these from our analysis, we find that a candidate will need at least 395 votes to be elected as the VP. Under our best case scenario, the UPA holds 363 votes in the forthcoming VP elections. As is the case with Presidential elections, the UPA will have to seek alliances to get a candidate of its choice elected to the office of the Vice-President. Scenarios for VP elections (figures represent the value of votes available with each party/ coalition)
| Party/ Coalition |
Scenario I |
Scenario II |
| UPA |
360 |
363 |
| NDA |
216 |
214 |
| Left |
38 |
38 |
| BSP |
36 |
36 |
| SP |
31 |
31 |
| BJD |
22 |
21 |
| AIADMK |
14 |
14 |
| Nominated |
14 |
14 |
| Others |
57 |
57 |
| Total |
788 |
788 |
| Minimum required to be elected |
395 |
395 |
Notes: [1] UPA: Congress, Trinamool, DMK, NCP,Rashtriya Lok Dal, J&K National Conference, Muslim League Kerala State Committee, Kerala Congress (M), All India Majlis-e-Ittehadul Muslimeen, Sikkim Democratic Front, Praja Rajyam Party, Viduthalai Chiruthaigal Katchi [2] NDA: BJP, JD(U), Shiv Sena, Shiromani Akali Dal [3] Left: CPI(M), CPI, Revolutionary Socialist Party,All India Forward Bloc