
India has been in lockdown since March 25, 2020. During this time, activities not contributing to the production and supply of essential goods and services were completely or partially suspended. Passenger trains and flights were halted. The lockdown has severely impacted migrants, several of whom lost their jobs due to shutting of industries and were stranded outside their native places wanting to get back. Since then, the government has announced relief measures for migrants, and made arrangements for migrants to return to their native place. The Supreme Court of India, recognising the problems faced by migrants stranded in different parts of the country, reviewed transportation and relief arrangements made by the government. On June 9, the Court directed central and state governments to complete transportation of remaining stranded migrants and expand focus of relief measures to facilitate employment for returning migrants. In this blog, we highlight some facts about migration in India, summarise key relief measures announced by the government and directives issued by the Supreme Court for the migrant population in relation to the lockdown.
Overview of Migration
Migration is the movement of people away from their usual place of residence, across either internal (within country) or international (across countries) borders. The latest government data on migration comes from the 2011 Census. As per the Census, India had 45.6 crore migrants in 2011 (38% of the population) compared to 31.5 crore migrants in 2001 (31% of the population). Between 2001 and 2011, while population grew by 18%, the number of migrants increased by 45%. In 2011, 99% of total migration was internal and immigrants (international migrants) comprised 1%.[1]
Patterns of migration
Internal migrant flows can be classified on the basis of origin and destination. One kind of classification is: i) rural-rural, ii) rural-urban, iii) urban-rural and iv) urban-urban. As per the 2011 census, there were 21 crore rural-rural migrants which formed 54% of classifiable internal migration (the Census did not classify 5.3 crore people as originating from either rural or urban areas). Rural-urban and urban-urban movement accounted for around 8 crore migrants each. There were around 3 crore urban-rural migrants (7% of classifiable internal migration).
Another way to classify migration is: (i) intra-state, and (ii) inter-state. In 2011, intra-state movement accounted for almost 88% of all internal migration (39.6 crore persons).1
There is variation across states in terms of inter-state migration flows. According to the 2011 Census, there were 5.4 crore inter-state migrants. As of 2011, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar were the largest source of inter-state migrants while Maharashtra and Delhi were the largest receiver states. Around 83 lakh residents of Uttar Pradesh and 63 lakh residents of Bihar had moved either temporarily or permanently to other states. Around 60 lakh people from across India had migrated to Maharashtra by 2011.
Figure 1: Inter-state Migration (in lakh)
Note: A net out-migrant state is one where more people migrate out of the state than those that migrate into the state. Net in-migration is the excess of incoming migrants over out-going migrants.
Sources: Census 2011; PRS.
Reasons for internal migration and size of migrant labour force
As of 2011, majority (70%) of intra-state migration was due to reasons of marriage and family with variation between male and female migrants. While 83% of females moved for marriage and family, the corresponding figure for males was 39%. Overall, 8% of people moved within a state for work (21% of male migrants and 2% of female migrants).
Movement for work was higher among inter-state migrants- 50% of male and 5% of female inter-state migrants. As per the Census, there were 4.5 crore migrant workers in 2011. However, according to the Working Group Report on Migration, the Census underestimates the migrant worker population. Female migration is recorded as movement due to family since that is the primary reason. However, many women take up employment after migrating which is not reflected in the number of women moving for work-related reasons. [2]
According to the Economic Survey, 2016-17, Census data also underestimates temporary migrant labour movement. In 2007-08, the NSSO estimated the size of India’s migrant labour at seven crore (29% of the workforce). The Economic Survey, 2016-17, estimated six crore inter-state labour migrants between 2001-2011. The Economic Survey also estimated that in each year between 2011-2016, on average 90 lakh people travelled for work.
Figure 2: Reasons for intra-state migration
Sources: Census 2011; PRS.
Figure 3:Reasons for inter-state migration
Sources: Census 2011; PRS.
Issues faced by migrant labour
Article 19(1)(e) of the Constitution, guarantees all Indian citizens the right to reside and settle in any part of the territory of India, subject to reasonable restrictions in the interest of the general public or protection of any scheduled tribe. However, people migrating for work face key challenges including: i) lack of social security and health benefits and poor implementation of minimum safety standards law, ii) lack of portability of state-provided benefits especially food provided through the public distribution system (PDS) and iii) lack of access to affordable housing and basic amenities in urban areas. 2
Poor implementation of protections under the Inter-State Migrant Workmen Act, 1979 (ISMW Act)
The ISMW Act provides certain protections for inter-state migrant workers. Labour contractors recruiting migrants are required to: (i) be licensed, (ii) register migrant workers with the government authorities, and (iii) arrange for the worker to be issued a passbook recording their identity. Guidelines regarding wages and protections (including accommodation, free medical facilities, protective clothing) to be provided by the contractor are also outlined in the law.
In December 2011, a report by the Standing Committee on Labour observed that registration of workers under the ISMW Act was low and implementation of protections outlined in the Act was poor. The report concluded that the Central government had not made any concrete and fruitful efforts to ensure that contractors and employers mandatorily register the workers employed with them enabling access to benefits under the Act.
Lack of portability of benefits
Migrants registered to claim access to benefits at one location lose access upon migration to a different location. This is especially true of access to entitlements under the PDS. Ration card required to access benefits under the PDS is issued by state governments and is not portable across states. This system excludes inter-state migrants from the PDS unless they surrender their card from the home state and get a new one from the host state.
Lack of affordable housing and basic amenities in urban areas
The proportion of migrants in urban population is 47%.1 In 2015, the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs identified migrants in urban areas as the largest population needing housing in cities. There is inadequate supply of low-income ownership and rental housing options. This leads to the spread of informal settlements and slums. The Prime Minister Awaas Yojana (PMAY) is a central government scheme to help the economically weaker section and low-income group access housing. Assistance under the scheme includes: i) slum rehabilitation, ii) subsidised credit for home loans, iii) subsidies up to Rs 1.5 lakh to either construct a new house or enhance existing houses on their own and iv) increasing availability of affordable housing units in partnership with the private sector. Since housing is a state subject, there is variation in approach of States towards affordable housing.2
Steps taken by the government with regard to migrant labour during the lockdown
During the lockdown, several inter-state migrant workers tried to return to their home state. Due to the suspension public transport facilities, migrants started walking towards their home state on foot. Subsequently, buses and Shramik special trains were permitted by the central government subject to coordination between states.[3],[4] Between May 1 and June 3, more than 58 lakh migrants were transported through specially operated trains and 41 lakh were transported by road. Measures taken by the government to aid migrants include-
Transport: On March 28, the central government authorised states to use the State Disaster Response Fund to provide accommodation to traveling migrants. States were advised to set up relief camps along highways with medical facilities to ensure people stay in these camps while the lockdown is in place.
In an order issued on April 29, the Ministry of Home Affairs allowed states to co-ordinate individually to transport migrants using buses. On May 1, the Indian Railways resumed passenger movement (for the first time since March 22) with Shramik Special trains to facilitate movement of migrants stranded outside their home state. Between May 1 and June 3, Indian Railways operated 4,197 Shramik trains transporting more than 58 lakh migrants. Top states from where Shramik trains originated are Gujarat and Maharashtra and states where the trains terminated are Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.[5] Note that these trends largely correspond to the migration patterns seen in the 2011 census data.
Food distribution: On April 1, the Ministry of Health and Family Affairs directed state governments to operate relief camps for migrant workers with arrangements for food, sanitation and medical services. On May 14, under the second tranche of the Aatma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan, the Finance Minister announced that free food grains would be provided to migrant workers who do not have a ration card for two months. The measure is expected to benefit eight crore migrant workers and their families. The Finance Minister also announced that One Nation One Ration card will be implemented by March 2021, to provide portable benefits under the PDS. This will allow access to ration from any Fair Price Shop in India.
Housing: The Aatma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan also launched a scheme for Affordable Rental Housing Complexes for Migrant Workers and Urban Poor to provide affordable rental housing units under PMAY. The scheme proposes to use existing housing stock under the Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Housing Mission (JnNURM) as well as incentivise public and private agencies to construct new affordable units for rent. Further, additional funds have been allocated for the credit linked subsidy scheme under PMAY for middle income group.
Financial aid: Some state governments (like Bihar, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh) announced one-time cash transfers for returning migrant workers. UP government announced the provision of maintenance allowance of Rs 1,000 for returning migrants who are required to quarantine.
Directions by the Supreme Court
The Supreme Court reviewed the situation of migrant labourers stranded in different parts of the country, noting inadequacies and lapses in government response to the situation.
[1] Census, 2011, Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, Ministry of Home Affairs.
[2] Report of Working Group on Migration, Ministry of Housing and Urban Poverty Alleviation, January 2017, http://mohua.gov.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/1566.pdf.
[3] Order No. 40-3/2020-DM-I (A), Ministry of Home Affairs, April 29, 2020, https://prsindia.org/files/covid19/notifications/4233.IND_Movement_of_Persons_April_29.pdf.
[4] Order No. 40-3/2020-DM-I (A), Ministry of Home Affairs, May 1, 2020, https://prsindia.org/files/covid19/notifications/IND_Special_Trains_May_1.jpeg.
[5] “Indian Railways operationalizes 4197 “Shramik Special” trains till 3rd June, 2020 (0900hrs) across the country and transports more than 58 lacs passengers to their home states through “Shramik Special” trains since May 1”, Press Information Bureau, Ministry of Railways, June 3, 2020, https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=1629043.
The central government has enforced a nation-wide lockdown between March 25 and May 3 as part of its measures to contain the spread of COVID-19. During the lockdown, several restrictions have been placed on the movement of individuals and economic activities have come to a halt barring the activities related to essential goods and services. The restrictions are being relaxed in less affected areas in a limited manner since April 20. In this blog, we look at how the lockdown has impacted the demand and supply of electricity and what possible repercussions its prolonged effect may have on the power sector.
Power supply saw a decrease of 25% during the lockdown (year-on-year)
As electricity cannot be stored in large amount, the power generation and supply for a given day are planned based on the forecast for demand. The months of January and February in 2020 had seen an increase of 3% and 7% in power supply, respectively as compared to 2019 (year-on-year). In comparison, the power supply saw a decrease of 3% between March 1 and March 24. During the lockdown between March 24 and April 19, the total power supply saw a decrease of about 25% (year-on-year).
Figure 1: % change in power supply position between March 1 and April 19 (Y-o-Y from 2019 to 2020)

Sources: Daily Reports; POSOCO; PRS.
If we look at the consumption pattern by consumer category, in 2018-19, 41% of total electricity consumption was for industrial purposes, followed by 25% for domestic and 18% for agricultural purposes. As the lockdown has severely reduced the industrial and commercial activities in the country, these segments would have seen a considerable decline in demand for electricity. However, note that the domestic demand may have seen an uptick as people are staying indoors.
Figure 2: Power consumption by consumer segment in 2018-19
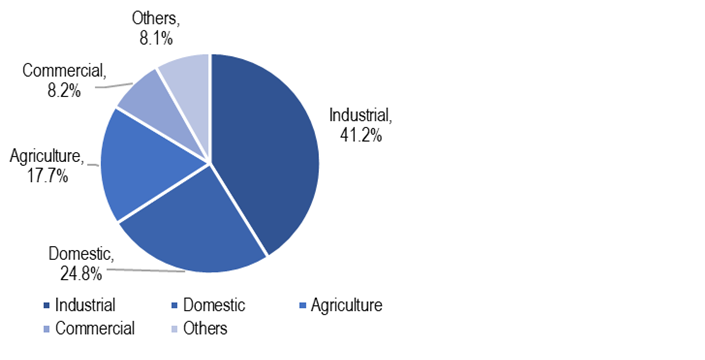
Sources: Central Electricity Authority; PRS.
Electricity demand may continue to be subdued over the next few months. At this point, it is unclear that when lockdown restrictions are eased, how soon will economic activities return to pre COVID-19 levels. India’s growth projections also highlight a slowdown in the economy in 2020 which will further impact the demand for electricity. On April 16, the International Monetary Fund has slashed its projection for India’s GDP growth in 2020 from 5.8% to 1.9%.
A nominal increase in energy and peak deficit levels
As power sector related operations have been classified as essential services, the plant operations and availability of fuel (primarily coal) have not been significantly constrained. This can be observed with the energy deficit and peak deficit levels during the lockdown period which have remained at a nominal level. Energy deficit indicates the shortfall in energy supply against the demand during the day. The average energy deficit between March 25 and April 19 has been 0.42% while the corresponding figure was 0.33% between March 1 and March 24. Similarly, the average peak deficit between March 25 and April 19 has been 0.56% as compared to 0.41% between March 1 and March 24. Peak deficit indicates the shortfall in supply against demand during highest consumption period in a day.
Figure 3: Energy deficit and peak deficit between March 1, 2020 and April 19, 2020 (in %)

Sources: Daily Reports; POSOCO; PRS.
Coal stock with power plants increases
Coal is the primary source of power generation in the country (~71% in March 2020). During the lockdown period, the coal stock with coal power plants has seen an increase. As of April 19, total coal-stock with the power plants in the country (in days) has risen to 29 days as compared to 24 days on March 24. This indicates that the supply of coal has not been constrained during the lockdown, at least to the extent of meeting the requirements of power plants.
Energy mix changes during the lockdown, power generation from coal impacted
During the lockdown, power generation has been adjusted to compensate for reduced consumption, Most of this reduction in consumption has been adjusted by reduced coal power generation. As can be seen in Table 1, coal power generation reduced from an average of 2,511 MU between March 1 and March 24 to 1,873 MU between March 25 and April 19 (about 25%). As a result, the contribution of coal in total power generation reduced from an average of 72.5% to 65.6% between these two periods.
Table 1: Energy Mix during March 1-April 19, 2020

Sources: Daily Reports; POSOCO; PRS.
This shift may be happening due to various reasons including: (i) renewable energy sources (solar, wind, and small hydro) have MUST RUN status, i.e., the power generated by them has to be given the highest priority by distribution companies, and (ii) running cost of renewable power plants is lower as compared to thermal power plants.
This suggests that if growth in electricity demand were to remain weak, the adverse impact on the coal power plants could be more as compared to other power generation sources. This will also translate into weak demand for coal in the country as almost 87% of the domestic coal production is used by the power sector. Note that the plant load factor (PLF) of the thermal power plants has seen a considerable decline over the years, decreasing from 77.5% in 2009-10 to 56.4% in 2019-20. Low PLF implies that coal plants have been lying idle. Coal power plants require significant fixed costs, and they incur such costs even when the plant is lying idle. The declining capacity utilisation augmented by a weaker demand will undermine the financial viability of these plants further.
Figure 4: Power generation from coal between March 1, 2020 and April 19, 2020 (in MU)
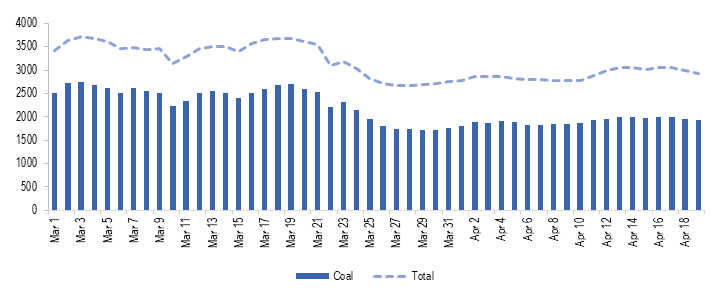
Sources: Daily Reports; POSOCO; PRS.
Finances of the power sector to be severely impacted
Power distribution companies (discoms) buy power from generation companies and supply it to consumers. In India, most of the discoms are state-owned utilities. One of the key concerns in the Indian power sector has been the poor financial health of its discoms. The discoms have had high levels of debt and have been running losses. The debt problem was partly addressed under the UDAY scheme as state governments took over 75% of the debt of state-run discoms (around 2.1 lakh crore in two years 2015-16 and 2016-17). However, discoms have continued to register losses owing to underpricing of electricity tariff for some consumer segments, and other forms of technical and commercial losses. Outstanding dues of discoms towards power generation companies have also been increasing, indicating financial stress in some discoms. At the end of February 2020, the total outstanding dues of discoms to generation companies stood at Rs 92,602 crore.
Due to the lockdown and its further impact in the near term, the financial situation of discoms is likely to be aggravated. This will also impact other entities in the value chain including generation companies and their fuel suppliers. This may lead to reduced availability of working capital for these entities and an increase in the risk of NPAs in the sector. Note that, as of February 2020, the power sector has the largest share in the deployment of domestic bank credit among industries (Rs 5.4 lakh crore, 19.3% of total).
Following are some of the factors which have impacted the financial situation during the lockdown:
Reduced cross-subsidy: In most states, the electricity tariff for domestic and agriculture consumers is lower than the actual cost of supply. Along with the subsidy by the state governments, this gap in revenue is partly compensated by charging industrial and commercial consumers at a higher rate. Hence, industrial and commercial segments cross-subsidise the power consumption by domestic and agricultural consumers.
The lockdown has led to a halt on commercial and industrial activities while people are staying indoors. This has led to a situation where the demand from the consumer segments who cross-subsidise has decreased while the demand from consumer segments who are cross-subsidised has increased. Due to this, the gap between revenue realised by discoms and cost of supply will widen, leading to further losses for discoms. States may choose to bridge this gap by providing a higher subsidy.
Moratorium to consumers: To mitigate the financial hardship of citizens due to COVID-19, some states such as Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Goa, among others, have provided consumers with a moratorium for payment of electricity bills. At the same time, the discoms are required to continue supplying electricity. This will mean that the return for the supply made in March and April will be delayed, leading to lesser cash in hand for discoms.
Some state governments such as Bihar also announced a reduction in tariff for domestic and agricultural consumers. Although, the reduction in tariff will be compensated to discoms by government subsidy.
Constraints with government finances: The revenue collection of states has been severely impacted as economic activities have come to a halt. Further, the state governments are directing their resources for funding relief measures such as food distribution, direct cash transfers, and healthcare. This may adversely affect or delay the subsidy transfer to discoms.
The UDAY scheme also requires states to progressively fund greater share in losses of discoms from their budgetary resources (10% in 2018-19, 25% in 2019-20, and 50% in 2020-21). As losses of discoms may widen due to the above-mentioned factors, the state government’s financial burden is likely to increase.
Capacity addition may be adversely impacted
As per the National Electricity Plan, India’s total capacity addition target is around 176 GW for 2017-2022. This comprises of 118 GW from renewable sources, 6.8 GW from hydro sources, and 6.4 GW from coal (apart from 47.8 GW of coal-based power projects already in various stages of production as of January 2018).
India has set a goal of installing 175 GW of Renewable Power Capacity by 2022 as part of its climate change commitments (86 GW has been installed as of January 2020). In January 2020, the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Energy observed that India could only install 82% and 55% of its annual renewable energy capacity addition targets in 2017-18 and 2018-19. As of January 2020, 67% of the target has been achieved for 2019-20.
Due to the impact of COVID-19, the capacity addition targets for various sources is likely to be adversely impacted in the short run as:
construction activities were stopped during the lockdown and will take some time to return to normal,
disruption in the global supply chain may lead to difficulties with the availability of key components leading to delay in execution of projects, for instance, for solar power plants, solar PV modules are mainly imported from China, and
reduced revenue for companies due to weak demand will leave companies with less capacity left for capital expenditure.
Key reforms likely to be delayed
Following are some of the important reforms anticipated in 2020-21 which may get delayed due to the developing situation:
The real-time market for electricity: The real-time market for electricity was to be operationalised from April 1, 2020. However, the lockdown has led to delay in completion of testing and trial runs. The revised date for implementation is now June 1, 2020.
UDAY 2.0/ADITYA: A new scheme for the financial turnaround of discoms was likely to come this year. The scheme would have provided for the installation of smart meters and incentives for rationalisation of the tariff, among other things. It remains to be seen what this scheme would be like since the situation with government finances is also going to worsen due to anticipated economic slowdown.
Auction of coal blocks for commercial mining: The Coal Ministry has been considering auction of coal mines for commercial mining this year. 100% FDI has been allowed in the coal mining activity for commercial sale of coal to attract foreign players. However, the global economic slowdown may mean that the auctions may not generate enough interest from foreign as well as domestic players.
For a detailed analysis of the Indian Power Sector, please see here. For details on the number of daily COVID-19 cases in the country and across states, please see here. For details on the major COVID-19 related notifications released by the centre and the states, please see here.