
In November 2017, the 15th Finance Commission (Chair: Mr N. K. Singh) was constituted to give recommendations on the transfer of resources from the centre to states for the five year period between 2020-25. In recent times, there has been some discussion around the role and mandate of the Commission. In this context, we explain the role of the Finance Commission.
What is the Finance Commission?
The Finance Commission is a constitutional body formed every five years to give suggestions on centre-state financial relations. Each Finance Commission is required to make recommendations on: (i) sharing of central taxes with states, (ii) distribution of central grants to states, (iii) measures to improve the finances of states to supplement the resources of panchayats and municipalities, and (iv) any other matter referred to it.
Composition of transfers: The central taxes devolved to states are untied funds, and states can spend them according to their discretion. Over the years, tax devolved to states has constituted over 80% of the total central transfers to states (Figure 1). The centre also provides grants to states and local bodies which must be used for specified purposes. These grants have ranged between 12% to 19% of the total transfers.
 Over the years the core mandate of the Commission has remained unchanged, though it has been given the additional responsibility of examining various issues. For instance, the 12th Finance Commission evaluated the fiscal position of states and offered relief to those that enacted their Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management laws. The 13th and the 14th Finance Commissionassessed the impact of GST on the economy. The 13th Finance Commission also incentivised states to increase forest cover by providing additional grants.
Over the years the core mandate of the Commission has remained unchanged, though it has been given the additional responsibility of examining various issues. For instance, the 12th Finance Commission evaluated the fiscal position of states and offered relief to those that enacted their Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management laws. The 13th and the 14th Finance Commissionassessed the impact of GST on the economy. The 13th Finance Commission also incentivised states to increase forest cover by providing additional grants.
15th Finance Commission: The 15th Finance Commission constituted in November 2017 will recommend central transfers to states. It has also been mandated to: (i) review the impact of the 14th Finance Commission recommendations on the fiscal position of the centre; (ii) review the debt level of the centre and states, and recommend a roadmap; (iii) study the impact of GST on the economy; and (iv) recommend performance-based incentives for states based on their efforts to control population, promote ease of doing business, and control expenditure on populist measures, among others.
Why is there a need for a Finance Commission?
The Indian federal system allows for the division of power and responsibilities between the centre and states. Correspondingly, the taxation powers are also broadly divided between the centre and states (Table 1). State legislatures may devolve some of their taxation powers to local bodies.

The centre collects majority of the tax revenue as it enjoys scale economies in the collection of certain taxes. States have the responsibility of delivering public goods in their areas due to their proximity to local issues and needs.
Sometimes, this leads to states incurring expenditures higher than the revenue generated by them. Further, due to vast regional disparities some states are unable to raise adequate resources as compared to others. To address these imbalances, the Finance Commission recommends the extent of central funds to be shared with states. Prior to 2000, only revenue income tax and union excise duty on certain goods was shared by the centre with states. A Constitution amendment in 2000 allowed for all central taxes to be shared with states.
Several other federal countries, such as Pakistan, Malaysia, and Australia have similar bodies which recommend the manner in which central funds will be shared with states.
Tax devolution to states
 The 14th Finance Commission considerably increased the devolution of taxes from the centre to states from 32% to 42%. The Commission had recommended that tax devolution should be the primary source of transfer of funds to states. This would increase the flow of unconditional transfers and give states more flexibility in their spending.
The 14th Finance Commission considerably increased the devolution of taxes from the centre to states from 32% to 42%. The Commission had recommended that tax devolution should be the primary source of transfer of funds to states. This would increase the flow of unconditional transfers and give states more flexibility in their spending.
The share in central taxes is distributed among states based on a formula. Previous Finance Commissions have considered various factors to determine the criteria such as the population and income needs of states, their area and infrastructure, etc. Further, the weightage assigned to each criterion has varied with each Finance Commission.
The criteria used by the 11th to 14thFinance Commissions are given in Table 2, along with the weight assigned to them. State level details of the criteria used by the 14th Finance Commission are given in Table 3.

Grants-in-Aid
Besides the taxes devolved to states, another source of transfers from the centre to states is grants-in-aid. As per the recommendations of the 14th Finance Commission, grants-in-aid constitute 12% of the central transfers to states. The 14th Finance Commission had recommended grants to states for three purposes: (i) disaster relief, (ii) local bodies, and (iii) revenue deficit.
As of May 11, 2020, there are 67,152 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in India. Since May 4, 24,619 new cases have been registered. Out of the confirmed cases so far, 20,917 patients have been cured/discharged and 2,206 have died. As the spread of COVID-19 has increased across the country, the central government has continued to announce several policy decisions to contain the spread, and support citizens and businesses who are being affected by the pandemic. In this blog post, we summarise some of the key measures taken by the central government in this regard between May 4 and May 11, 2020.
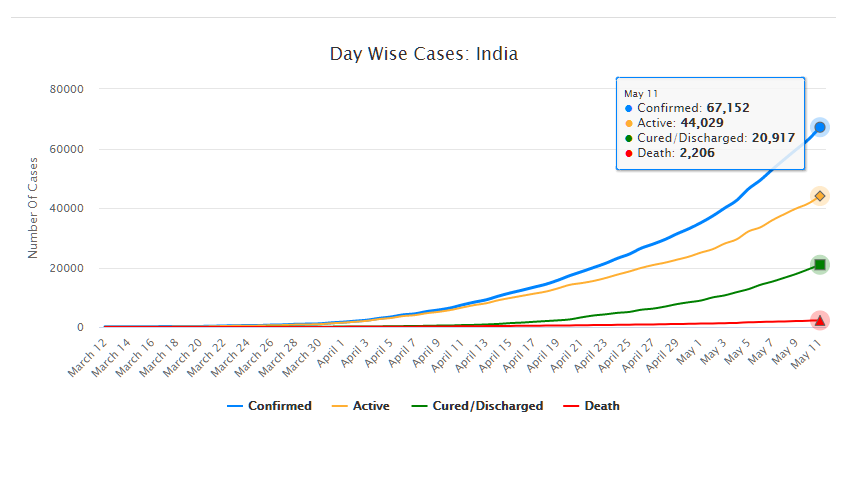
Source: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; PRS.
Industry
Relaxation of labour laws in some states
The Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Uttarakhand governments have passed notifications to increase maximum weekly work hours from 48 hours to 72 hours and daily work hours from 9 hours to 12 hours for certain factories. This was done to combat the shortage of labour caused by the lockdown. Further, some state governments stated that longer shifts would ensure a fewer number of workers in factories so as to allow for social distancing.
Madhya Pradesh has promulgated the Madhya Pradesh Labour Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020. The Ordinance exempts establishments with less than 100 workers from adhering to the Madhya Pradesh Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1961, which regulates the conditions of employment of workers. Further, it allows the state government to exempt any establishment or class of establishments from the Madhya Pradesh Shram Kalyan Nidhi Adhiniyam, 1982, which provides for the constitution of a welfare fund for labour.
The Uttar Pradesh government has published a draft Ordinance which exempts all factories and establishments engaged in manufacturing processes from all labour laws for a period of three years. Certain conditions will continue to apply with regard to payment of wages, safety, compensation and work hours, amongst others. However, labour laws providing for social security, industrial dispute resolution, trade unions, strikes, amongst others, will not apply under the Ordinance.
Financial aid
Central government signs an agreement with Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank for COVID-19 support
The central government and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) signed a 500 million dollar agreement for the COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project. The project aims to help India respond to the COVID-19 pandemic and strengthen India’s public health system to manage future disease outbreaks. The project is being financed by the World Bank and AIIB in the amount of 1.5 billion dollars, of which one billion dollars is being provided by World Bank and 500 million dollars is being provided by AIIB. This financial support will be available to all states and union territories and will be used to address the needs of at-risk populations, medical personnel, and creating medical and testing facilities, amongst others. The project will be implemented by the National Health Mission, the National Center for Disease Control, and the Indian Council of Medical Research, under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Travel
Restarting of passenger travel by railways
Indian Railways plans to restart passenger trains from May 12 onwards. It will begin with 15 pairs of trains which will run from New Delhi station connecting Dibrugarh, Agartala, Howrah, Patna, Bilaspur, Ranchi, Bhubaneswar, Secunderabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Madgaon, Mumbai Central, Ahmedabad and Jammu Tawi. Booking for reservation in these trains will start at 4 pm on May 11. Thereafter, Indian Railways plans to start more services on new routes.
Return of Indians stranded abroad
The central government will facilitate the return of Indian nationals stranded abroad in a phased manner beginning on May 7. The travel will be arranged by aircraft and naval ships. The stranded Indians utilising the service will be required to pay for it. Medical screening of the passengers will be done before the flight. On reaching India, passengers will be required to download the Aarogya Setu app. Further, they will be quarantined by the concerned state government in either a hospital or a quarantine institution for 14 days on a payment basis. After quarantine, passengers will be tested for COVID-19 and further action will be taken based on the results.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.